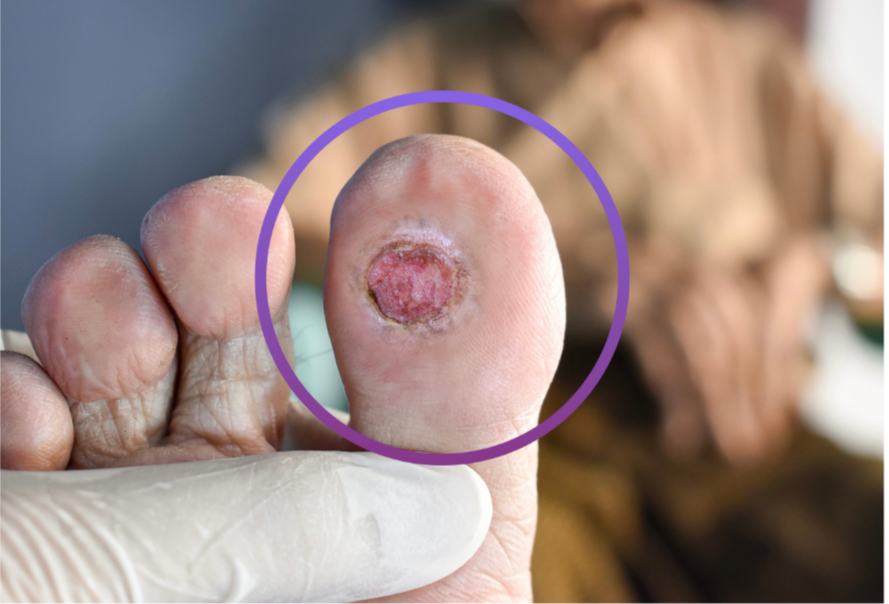
The Disease Burden of Chronic Wounds and Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Chronic Wound Burden and Public Health Impact
Chronic wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), represent a significant and growing public health challenge worldwide, with an estimated 18.6 million people affected worldwide.¹ These wounds are associated with delayed healing, frequent complications, high rates of infection, and substantial healthcare utilization.² In patients with diabetes, non-healing wounds contribute to increased morbidity, risk of amputation, and rising direct and indirect healthcare costs.²
Diabetes is a leading risk factor for the development of chronic wounds, particularly diabetic foot ulcers. Impaired circulation, neuropathy, inflammation, and altered cellular signaling contribute to delayed wound healing in patients with diabetes, making DFUs difficult to treat and prone to recurrence.³ As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, the burden of chronic wounds on patients and healthcare systems is expected to increase.
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is associated with substantial healthcare expenditures, including outpatient wound care visits, hospitalizations, surgical interventions, and long-term management.⁴ Chronic wounds often require prolonged treatment courses, repeated procedures, and intensive monitoring, contributing to significant direct medical costs as well as indirect costs related to lost productivity and reduced quality of life.⁵
Despite advances in wound care, many patients with diabetic foot ulcers are not being served through currently available treatments. The complexity of chronic wound biology and the limitations of current therapies highlight the ongoing unmet medical need.
DFU Facts:
Approximately one-third of people living with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer in their lifetime.⁶
Every 3 minutes and 30 seconds in the United States, a limb is amputated due to diabetes.¹¹
Roughly 50% of DFUs become infected, and about 20% of infected moderate-to-severe ulcers lead to amputation.¹¹
DFUs precede ~80 % of diabetes-related lower extremity amputations.¹
People with DFUs have a 5-year mortality rate that exceeds 70 % after major amputation (above-foot).⁷
The Cost of Diabetes Care
$53,779
$53,779
is the average cost of inpatient care for a major amputation per patient⁸
60%
60%
of people with diabetes develop neuropathy that can lead to a DFU¹⁰
49%
49%
of people with a DFU experience recurrence in the first year⁶
85%
85%
of diabetes-related amputations are preceded by a DFU, and can be avoided⁹
Diabetes directly cost $237 billion in the U.S. with one-third of these direct costs due to foot disease.
References
Armstrong DG, Tan TW, Boulton AJM, Bus SA. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023 Jul 3;330(1):62-75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.10578. PMID: 37395769; PMCID: PMC10723802.
Waibel FWA, et al. Current knowledge of morbidities and direct costs related to diabetic foot disorders: a literature review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 17;14:1323315.
Dawi J, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Pathophysiology, Immune Dysregulation, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 29;13(5):1076.
Lo ZJ, et al. Clinical and economic burden of diabetic foot ulcers: A 5-year longitudinal multi-ethnic cohort study from the tropics. Int Wound J. 2021 Jun;18(3):375-386.
Redmond MC, Gethin G, Finn DP. A Review of Chronic Wounds and Their Impact on Negative Affect, Cognition, and Quality of Life. Int Wound J. 2025 Aug;22(8):e70748.
Srinivas-Shankar U, Kimyaghalam A, Bergman R. Diabetic Foot Ulceration and Complications [Updated 2025 Oct 28]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK499887/
Armstrong DG, Swerdlow MA, Armstrong AA, Conte MS, Padula WV, Bus SA. Five year mortality and direct costs of care for people with diabetic foot complications are comparable to cancer. J Foot Ankle Res. 2020;13(1):16.
Hicks CW, Selvarajah S, Mathioudakis N, et al. Trends and determinants of costs associated with the inpatient care of diabetic foot ulcers. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 2014 Nov;60(5):1247-1254.e2.
David G. Armstrong, D.P.M., M.D., Ph.D., Andrew J.M. Boulton, M.D., and Sicco A. Bus, Ph.D. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N Engl J Med 2017;376:2367-75.
APMA, Diabetic Wound Care. Available at: https://www.apma.org/patients-and-the-public/conditions-affecting-the-foot-and-ankle/diabetic-wound-care/. Accessed: January 2026.
American Diabetes Association. Available at: https://diabetes.org/advocacy/amputation-prevention-alliance Accessed: February 2026
You might also be interested in: